Frequently asked Questions
There are three main chains connecting science with economy:
a. The engineers needed by high-tech industries are educated by scientists, or are former scientists.
b. High-tech intellectual property is created in science schools. It is transferred and applied in the economy in two main ways: (1) through the contract work of a private company and scientific groups with relevant skills and abilities, (2) the commercialization of newly created intellectual property by the member(s) of the scientific group through a startup.
c. Increasing the country's human capital level and overall international ranking. The first contributes to the growth of international investments in the high-tech industry of the country, the export of high-tech production and services. The second has the same universal importance as the development of culture and sports.
Only about the usefulness of basic research can be read the former director of CERN (European Organization for Nuclear Research) "The use of basic science. Benefits of basic science" in the article [6].
The state is the developer of public order policies and programs for fundamental, applied researches and experimental developments, the direct customer, and in some cases also the executor.
Since the private order itself cannot have a permanent character, and the co-responsible scientific school may be completely absent from the beginning, an approach has been established in the world for a long time, according to which the creation, maturation and stability of scientific activities, infrastructures and communities take place according to a planned public order. through the implementation of structures conducting contests of scientific programs or national technological programs. The extent to which the state creates and develops the scientific community and infrastructure through public procurement is one of the most important factors in the competition of states in terms of international investments in high-tech industry.
Development of science:
- Implementation of basic and applied research programs in the branches of science important for the country.
- Development of human capital necessary for basic and applied research: immigration (especially repatriation), training and education of scientists.
- Development of necessary infrastructures for basic and applied research and creation of new ones in accordance with the implementation of the above programs.
The best method created by mankind, through which the quality of knowledge created as a result of scientific research is determined, is scientific review (peer review). It is carried out practically all over the world by organizers of international conferences or editorial offices of journals. The higher the ranking of an international conference or journal (for example, the impact factor), the more influential the new knowledge created is considered.
The quality of a scientist is determined by the number of publications in journals with a national and international impact factor and the number of references to these publications.
According to the 2020 Global Innovation Index of the World Patent Organization (WIPO Global Innovation Index 2020, hereinafter referred to as GII), the Republic of Armenia ranks 18th in terms of scientific and technical publications.4th place [4], which qualifies as a strength, particularly in the relevant income group. However, it is necessary to note that Armenia was ranked in last year's GII report 13th place [4].
Types of R&D according to the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development's Frascati manual classification [1]:
- Basic or fundamental research (basic research) - experimental or theoretical work, which is carried out mainly to acquire new fundamental knowledge about phenomena, without pursuing the goal of application.
- Applied research (applied research) - experimental or theoretical unique work to acquire new knowledge, which is mainly directed towards a specific, practical goal,
- Experimental development work or Experimental development - systematic work based on the knowledge obtained from research and practical experience, aimed at creating or improving new products or processes.
Basic research in turn is of two types [1]:
- Pure basic research (pure basic research) - is conducted for the purpose of acquiring knowledge, without seeking social or economic benefits or making active efforts to apply the results to practical problems or to transfer the results to the fields responsible for application.
In the modern world, these are mostly large-scale research into the most fundamental laws of nature, with extensive international collaboration, such as the CERN project. Participating in these researches is important because it will help prevent brain drain and the results of international programs will be available to Armenia. - Oriented basic research (oriented basic research) - is performed with the expectation that a broad knowledge base will be created, which is likely to be the basis for solving known or expected current or future problems.
Usually, they are relatively small-scale basic research, close to applied research, a few percent of which give results worthy of transfer to the stage of applied research.
Many examples of differentiating the types of R&D work can be found in the aforementioned manual [2].
All these concepts are equivalent.
GRP works. It is opened as "research and experimental construction works". It is a direct translation from the Russian concept of НИОКР (Научно-изделительские и опытно-конструкторские работы). It is equivalent to the English concept of R&D. This term is often used in various legal acts of the Republic of Armenia, especially in the context of the work of the Defense Security Service.
GHPM. It opens as "scientific research and experimental development". It is almost a direct translation of the English R&D term from Research & Experimental Development.
HevM. It opens as "research and development". It is a literal translation of the term "Research & Development" in English.
"scientific and scientific-technical activity". It is used in the Law of RA "On Scientific and Scientific-Technical Activities" [7], related laws[8,9] and the draft of the new Law on Higher Education and Science[11] .
R&D. Բացվում է «Research & Development», որի ուղիղ թարգմանությունն է «Հետազոտություն և Մշակում» (ՀևՄ)։ Կիրառվում են նաեւ «Research & Experimental Development» (տե՜ս OECD ձեռնարկ) կամ «Research & Technological Development» (օգտագործվում է Եվրոպայում [11]) բացումները։
The situation in Armenia
The total number of scientific workers included in state scientific programs and topics as of August 2020: 3959 people.
If we accept that the population of Armenia is 3 million people, then there are about 1320 scientists in Armenia per 1 million inhabitants. The same figure for the European Union was approximately 4,000 in 2018 [3].
Age composition of researchers with scientific degrees involved in scientific and scientific-technical activities.
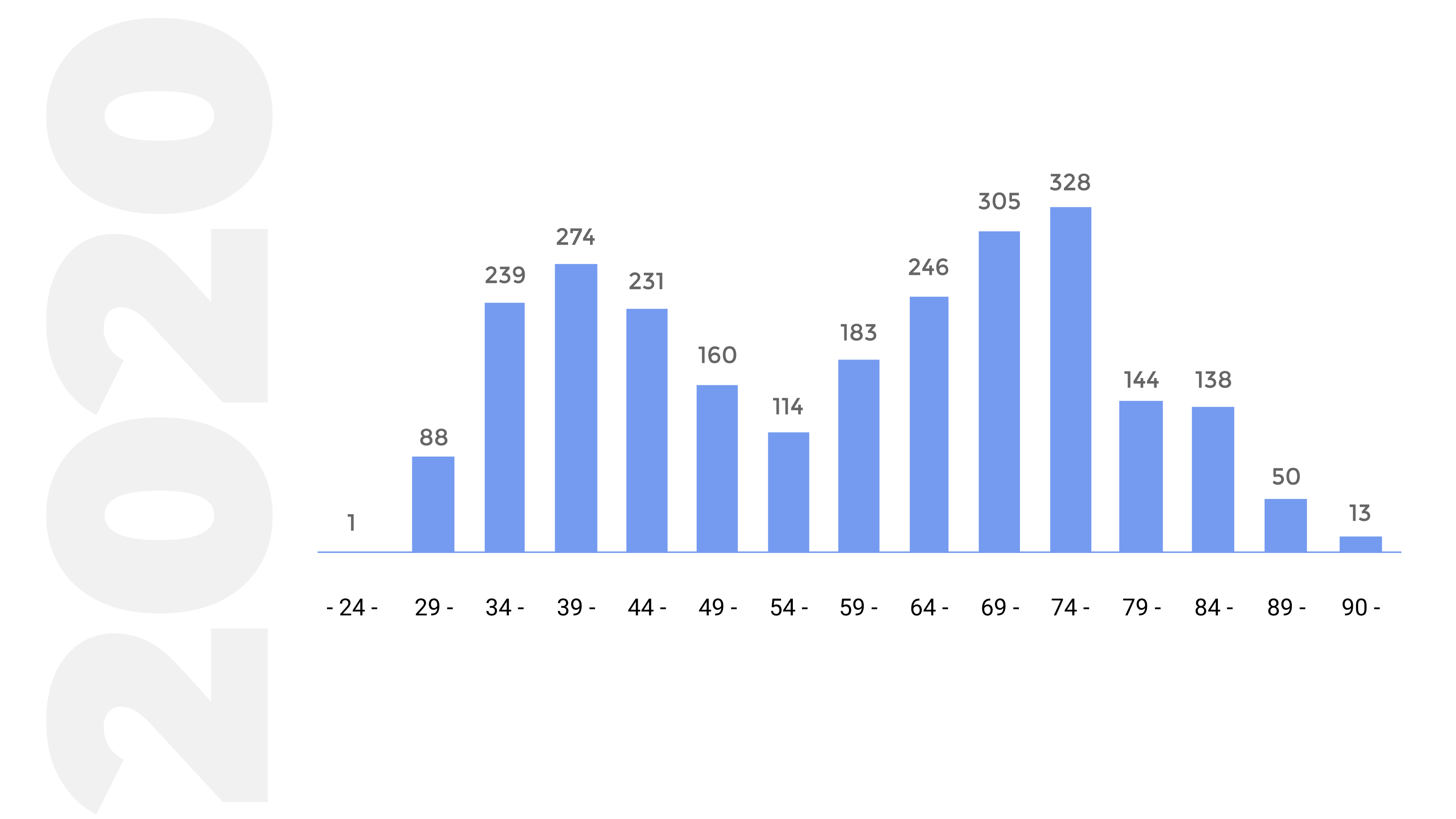
The age group of researchers with a scientific degree of retirement age is quite large - 38.9%.
According to 2020 It was planned to spend 14,255,302,700 drams on the RA budget, "Scientific and Scientific and Technical Research Program", which is 0.77% of the expenditure part of the budget [5].
According to the 2020 Global Innovation Index, the gross expenditure on R&D (GERD) of the Republic of Armenia was 0.2% of the GDP. According to that index, Armenia ranks first 91st place [4].
According to the InCites database of Web of Science, the number of scientific articles published by scientific research organizations and universities of the Republic of Armenia and included in Web of Science in 2015-2019 was 4 863: According to the data of the InCites database of the Web of Science, in the fields of social sciences and humanities in 2015-2019, respectively, 120 and: 83 scientific articles, making up a total of 4.2%the
Types of research and experimental development (R&D) according to the Frascati manual classification of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development [1]:
- Basic or fundamental research (basic research) - experimental or theoretical work, which is carried out mainly to acquire new fundamental knowledge about phenomena, without pursuing the goal of application.
- Applied research (applied research) - experimental or theoretical unique work to acquire new knowledge, which is mainly directed towards a specific, practical goal,
- Experimental development (experimental development) - systematic work based on the knowledge obtained from research and practical experience, which is aimed at creating or improving new products or processes.
Basic research in turn is of two types [1]:
- Pure basic research (pure basic research) - is conducted for the purpose of acquiring knowledge, without seeking social or economic benefits or making active efforts to apply the results to practical problems or to transfer the results to the fields responsible for application.
In the modern world, these are mostly large-scale research into the most fundamental laws of nature, with extensive international collaboration, such as the CERN project. Participating in these researches is important because it will help prevent brain drain and the results of international programs will be available to Armenia. - Oriented basic research (oriented basic research) - is performed with the expectation that a broad knowledge base will be created, which is likely to be the basis for solving known or expected current or future problems.
Usually, they are relatively small-scale basic research, close to applied research, a few percent of which give results worthy of transfer to the stage of applied research.
Many examples of differentiating the types of R&D work can be found in the aforementioned manual [2].
Here are 5 examples of programs that will have concrete results.
1- Repatriation and immigration of scientists
Provision of competitive grants for scientists working in the best international scientific institutes and universities to create scientific laboratories in Armenia, in order to fill the gaps of scientists and leading scientific directions in scientific research centers and universities.
As a result:
- human capital and infrastructures will be created or supplemented in the existing scientific directions, which will enable the implementation of private and state orders
- the number of scientists in Armenia will increase, the indicators of human capital will improve without long-term investments
- the potential of the Diaspora will be used,
- A scientific career in Armenia will become more attractive for young people, as there will be an opportunity to join groups of advanced scientists
- the number of quality scientific publications will increase and the country will improve its position in a number of ranking lists,
- there will be quality university educational programs for major professions.
2- Remote PI
Leading the research work of Armenian scientific groups by scientists working in the best international scientific institutes and universities through regular visits and remote communication.
As a result,
- human capital and infrastructures will be created or supplemented in the existing scientific directions, which will enable the implementation of private and state orders
- Scientific career in Armenia will become more attractive for young people
- the potential of the Diaspora will be used
- Armenian researchers will get the opportunity to work with top universities and research centers while staying in Armenia.
- Armenian scientists will gain modern experience, knowledge and connections.
- the number of quality scientific publications will increase and the country will improve its position in a number of ranking lists
- connections with the best scientific centers will be strengthened, which can be further used for expertise and cooperation with the private sector
3- Leading long-term research grants
Large grants for competitive scientists based in Armenia to form a scientific group and conduct long-term (5 years) research on advanced scientific topics.
As a result,
- will fill the gap in long-term grants to carry out ground-breaking and high-risk research projects
- the gap in grants needed for applied research, which is a necessary link in the commercialization of science results, will be filled
- the bureaucracy necessary to engage in scientific activity will be reduced
- Scientific career in Armenia will become more attractive for young people
- will prevent the outflow of ambitious scientists to other countries
- human capital and infrastructures will be created or supplemented in the existing scientific directions, which will enable the implementation of private and state orders
- the number of quality scientific publications will increase and the country will improve its position in a number of ranking lists,
4- Modernization of scientific infrastructures
Grants for the modernization of equipment necessary for scientific activities.
As a result,
- worn out and outdated equipment will be updated
- Scientific career in Armenia will become more attractive for young people
- will prevent the outflow of ambitious scientists to other countries
- modern infrastructure will be created that can be used by private sector companies
5- Expand the already implemented programs, in particular:
- research support program for PhD students and young applicants
- support program for starting scientific groups
- a program to support the strengthening of scientific groups or laboratories
- support program for scientific projects aimed at obtaining an applied result (in collaboration with a private individual)
- dual purpose program support program
It is almost unrelated and there are three main reasons for this:
- Most high-tech companies are information technology companies. IT companies usually collaborate with the Computer Science community. In Armenia, Computer Sciences and especially their most modern directions are underdeveloped. Instead, physics produces the greatest scientific results in Armenia
- 40% of scientists with degrees are over 65 years old. They were educated and began their scientific career in the USSR, where there was no private order. To expect that they can adapt to the science-industry relationship characteristic of today's capitalist society is unrealistic.
- In the conditions of 30 years of underfunding in Armenia, the scientific community engaged in basic research has remained almost exclusively, because applied research requires much larger grants. And basic research is the furthest from commercialization.
- Frascati Manual 2015. Guidelines for Collecting and Reporting Data on Research and Experimental Development, OECD, page 50
- Frascati Manual 2015. Guidelines for Collecting and Reporting Data on Research and Experimental Development, OECD, page 53, paragraph 2.40
- World Bank, https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.SCIE.RD.P6?locations=EU
- Global Innovation Index, www.globalinnovationindex.org
- RA 2020 Law on State Budget, https://www.gov.am/files/docs/3929.pdf
- CH Llewellyn Smith, former Director-General of CERN, CERN - Benefits of basic science
- RA Law "On Scientific and Scientific-Technical Activities", https://www.arlis.am/documentview.aspx?docid=804
- RA Law "On Scientific and Scientific-Technical Expertise", https://www.arlis.am/documentview.aspx?docid=120908
- RA Law "On the National Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Armenia", https://www.arlis.am/DocumentView.aspx?docid=121477
- Draft Law "On Higher Education and Science", https://www.e-draft.am/projects/3663
- Policy for research and technological development, https://www.europarl.europa.eu/factsheets/en/sheet/66/policy-for-research-and-technological-development





